The Best Fluffy Pancakes recipe you will fall in love with. Full of tips and tricks to help you make the best pancakes.

Blockchain Tutorial: Master the Future of Technology in Easy Steps
In a world where digital currencies are making headlines and tech jargon is flying around like confetti, understanding blockchain has never been more crucial. This revolutionary technology isn’t just for cryptocurrency enthusiasts; it’s reshaping industries from finance to healthcare. So why should anyone care? Because knowing how blockchain works could make them the smartest person in the room—unless they’re in a room full of blockchain developers, in which case they might need a little more than just a tutorial.
Blockchain Tutorial
Blockchain refers to a decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers. This innovative system enhances transparency and minimizes fraud.
Definition and Overview
Blockchain functions as a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. This technology allows data to be recorded in an irreversible manner, ensuring integrity. Participants can access the same data in real time, fostering trust among users. Initially developed for cryptocurrencies, its uses expand across various sectors, including supply chain management and healthcare records. Notably, the elimination of intermediaries streamlines processes, lowering costs and increasing efficiency.
Key Features of Blockchain
Blockchain possesses several key features setting it apart from traditional technologies. First, decentralization distributes control among all participants, reducing the risk of a single point of failure. Next, immutability guarantees that once data is added to the chain, it cannot be altered without consensus. Transparency is another significant aspect, as users can validate transactions independently. Furthermore, smart contracts automate processes through self-executing agreements, enhancing efficiency and reducing delays. Lastly, security remains a priority, with cryptographic techniques protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access.
Types of Blockchain
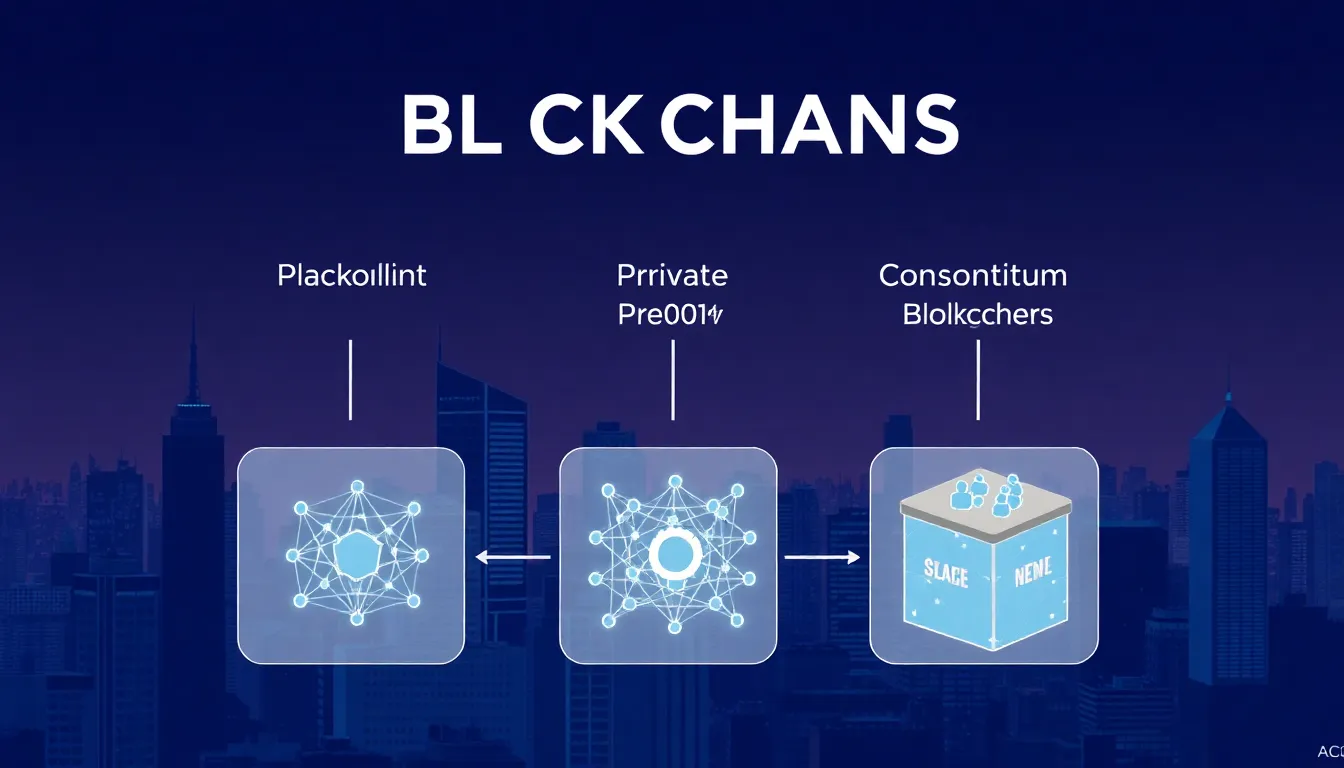
Understanding the different types of blockchain technology enhances insight into its varied applications. Each type serves specific purposes within the digital landscape.
Public vs. Private Blockchain
Public blockchains operate on open networks, allowing anyone to participate. Transactions become transparent, increasing trust among users. Bitcoin and Ethereum exemplify this type, promoting decentralization. In contrast, private blockchains restrict access to selected participants. Organizations favor these for internal applications, prioritizing privacy and control. Benefits include faster transaction speeds and enhanced security due to limited participation. Industries like finance or healthcare often prefer private blockchains for sensitive data management.
Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains represent a governance model shared by multiple organizations. These blockchains combine the benefits of both public and private types. Participants can join the network based on predetermined rules, enhancing security while promoting collaboration. Industries like banking often utilize consortium blockchains for interbank transactions. Members can verify transactions while maintaining some level of confidentiality. This model fosters trust among participants, significantly reducing processing times and operational costs.
Getting Started with Blockchain
Understanding the foundational aspects of blockchain technology sets the stage for practical applications and development. Key steps include setting up a development environment and familiarizing oneself with essential tools and libraries.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Start by installing a code editor, such as Visual Studio Code or Atom. Next, ensure that Node.js is installed, as it allows for JavaScript execution outside a browser. Developers may also benefit from using Docker to create isolated environments, simplifying dependencies. After these installations, selecting a blockchain framework like Truffle or Hardhat streamlines contract development and testing. Configuring these tools enables seamless interaction with blockchain networks, laying the foundation for further exploration.
Essential Tools and Libraries
When diving into blockchain development, several tools and libraries provide critical functionalities. Web3.js facilitates interaction with Ethereum nodes through JavaScript, supporting smart contract integration. Additionally, libraries like ethers.js offer lightweight alternatives for Ethereum applications. For testing, Mocha and Chai provide robust frameworks that enhance contract validation. Using Ganache sets up a personal Ethereum blockchain for rapid prototyping and testing, while Remix IDE serves as an excellent platform for coding and debugging contracts in a browser. Selecting these tools enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of development work.
Fundamental Concepts in Blockchain
Understanding fundamental concepts in blockchain technology is essential for navigating its complexities. Key features, such as cryptography and smart contracts, play pivotal roles in maintaining security and enhancing functionality.
Cryptography
Cryptography underpins blockchain security, ensuring data integrity and user privacy. It employs advanced algorithms to encrypt sensitive transaction information, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Each transaction incorporates a unique hash, linking it to the previous block and forming an unbreakable chain. This process renders tampering virtually impossible. Additionally, public and private keys facilitate secure user authentication, allowing individuals to sign transactions confidently. Proven techniques like asymmetric encryption uphold user trust in the system. Overall, cryptography serves as the backbone of blockchain’s security framework, protecting data and promoting transparency.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate and enforce agreements without the need for intermediaries. Each contract consists of self-executing code, executing specified actions when predefined conditions are met. This functionality streamlines workflows, reduces delays, and minimizes costs associated with traditional contract enforcement. Users can deploy smart contracts on various platforms, including Ethereum, which provides a robust environment for development. By eliminating human error, smart contracts enhance reliability and efficiency in transactions. Furthermore, transparency in execution allows all parties to verify outcomes, further building trust. Smart contracts exemplify blockchain’s transformative potential across numerous sectors.
Building Your First Blockchain Application
Creating a blockchain application involves understanding the technology and following a systematic approach. Developers can initiate the process by defining the application’s purpose and selecting the appropriate blockchain framework.
Step-by-Step Tutorial
- Identify objectives for the application, ensuring clarity in goals.
- Choose a blockchain framework such as Ethereum or Hyperledger for development.
- Set up a local development environment with tools like Visual Studio Code and Node.js.
- Write smart contracts using Solidity for Ethereum platforms.
- Use frameworks like Truffle for deploying and testing contracts efficiently.
- Interact with the blockchain through libraries like Web3.js or ethers.js.
- Test the application thoroughly to ensure functionality before launch.
This structured approach facilitates smooth development and ensures a clear direction.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Encounters with challenges during blockchain development are common but manageable. Developers may face issues like contract bugs or integration errors with blockchain networks. Comprehensive testing can identify bugs before deployment.
Another challenge involves managing transaction speeds and costs, which can impact application performance. To mitigate this, utilizing layer 2 solutions like Polygon for Ethereum can enhance throughput.
Staying updated with blockchain technology trends and community best practices also aids in overcoming hurdles. Engaging with resources, forums, and documentation ensures better preparedness and problem-solving capabilities. These approaches enhance the overall development experience and lead to more robust blockchain applications.
Conclusion
Mastering blockchain technology opens doors to numerous opportunities across various industries. As it continues to evolve the way transactions are conducted and data is managed, staying informed about its advancements is crucial. Developers equipped with the right tools and knowledge can create impactful applications that leverage blockchain’s unique features.
Embracing the challenges and complexities of blockchain development can lead to innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and security. Engaging with the community and keeping up with emerging trends will further empower individuals to navigate this dynamic landscape effectively. With dedication and the right resources, anyone can contribute to the future of blockchain technology.








